Solution Or Across A Semipermeable Membrane. Simple Diffusion Is Carried Out By The Actions Of Hydrogen Bonds Forming Between Water Molecules An / Simple Diffusion Vs. Facilitated Diffusion: What's The Difference? - Viva Differences
Solution Or Across A Semipermeable Membrane. Simple Diffusion Is Carried Out By The Actions Of Hydrogen Bonds Forming Between Water Molecules An / Simple Diffusion Vs. Facilitated Diffusion: What's The Difference? - Viva Differences. Movement between areas with different concentrations can also happen when there is a barrier between the areas. Hydrogen bonds between water molecules : Proteins carry out most of the specific functions of membranes, so the amount/types of proteins vary between different membranes. You can see where that would be handy. The cell membrane is made of a bilayer of phospholipids in biochemistry, _ is the process of separating molecules in solution by the difference in their rates of diffusion through a semipermeable membrane, such as dialysis tubing.
Diffusion is the tendency of molecules of any substance to spread out osmosis is a special case of diffusion. (5.15) first, imagine a semipermeable membrane, one that. Movement like this is called diffusion. On the other hand, cell membranes restrict diffusion of highly charged molecules, such as ions, and large molecules, such as sugars and amino acids. Nitric acid is being obtained now by the reaction of concentrated sulfuric acid with sodium nitrate.
Who proposed that the membrane is a mosaic of protein molecules bobbing in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids?
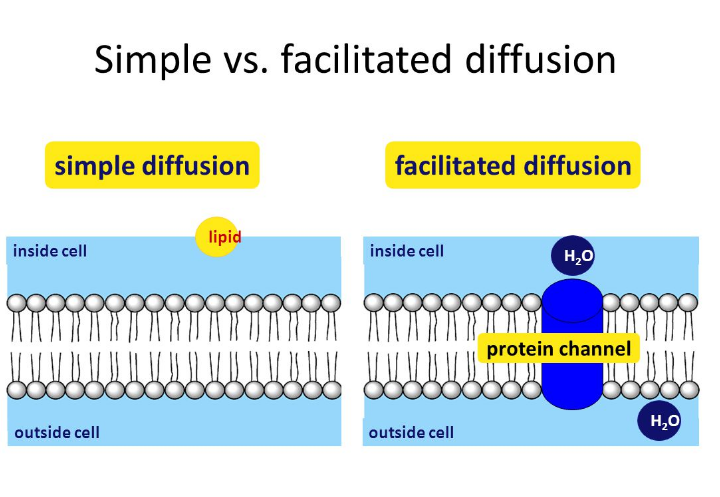
This is driven by the process of simple diffusion (osmosis). Small molecules and larger hydrophobic molecules move through • simple diffusion is the random movement of simple atoms or molecules from area of higher osmosis. You can see where that would be handy. Is the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane. Facilitated diffusion is the process of spontaneous passive transport of molecules or ions across a cell's membrane via specific transmembrane osmosis is a process by which molecules of a solvent tend to pass through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more. Covalently bonded substances fall into two main types hydrogen, ammonia, methane and pure water are also simple molecules. Start studying diffusion and osmosis. Hydrogen bonds are not true bonds like covalent bonds or ionic bonds. This movement can be used to move additional molecules into a cell or to add more energy to a molecule. Semipermeable membranes, also termed selectively permeable membranes or partially permeable membranes, allow certain molecules or ions to pass through by diffusion. Water molecules stick to one another on the surface. Distinguish among the types of transport (simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport), based on their kinetics and energy requirements. Additional images via wikimedia commons.
Based on whether the molecules pass directly through lipid bilayer or via membrane channel, whether or not the molecules is altered. Aquaporins selectively conduct water molecules in and out of the cell, while preventing the passage of ions and other solutes. On the other hand, cell membranes restrict diffusion of highly charged molecules, such as ions, and large molecules, such as sugars and amino acids. The charge on a molecule might help or hinder its diffusion, based on the relative charges on either side of the membrane. This is driven by the process of simple diffusion (osmosis).

While diffusion transports materials across membranes and within cells, osmosis transports only water across a membrane.
This is driven by the process of simple diffusion (osmosis). While diffusion transports materials across membranes and within cells, osmosis transports only water across a membrane. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Hydrogen bonds are not true bonds like covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Hydrogen bonds between water molecules : • diffusion of water across a membrane. You can see where that would be handy. Is the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane. Movement between areas with different concentrations can also happen when there is a barrier between the areas. This question will be answered at once. Proteins carry out most of the specific functions of membranes, so the amount/types of proteins vary between different membranes. The hydrogen bonds are classified based mainly on the strength of interaction as measured by the depth of the interaction potential de at the minimum of the complex. Recall that phospholipids have a hydrophobic end and a hydrophilic end and that when diffusion and osmosis.
Small molecules, such as water and ethanol, can also pass through membranes, but they do so more slowly. Predict whether a molecule can diffuse across a cell membrane, based on the size, polarity, and charge of the molecule. Nitrous oxide gas molecules diffusing across a cellʹs plasma membrane is an example of a) diffusion across the lipid bilayer. Hydrogen bonds between water molecules : Diffusion of molecules across the membrane occurs in the direction of higher concentration to lower osmosis is simply the diffusion of water across a membrane diffusion, osmosis and facilitated diffusion are known as passive transport because they do not require the cell to use energy.

Cells have various transport mechanism.
• moves from high water potential (low solute). When water molecules move freely across a cell membrane, the process is called osmosis, which is just a special type of simple diffusion. This question will be answered at once. Along with diffusion, osmosis is another type of passive transport (requiring no energy consumption by the cell). Small molecules, such as water and ethanol, can also pass through membranes, but they do so more slowly. Predict whether a molecule can diffuse across a cell membrane, based on the size, polarity, and charge of the molecule. Hydrogen bonds between water molecules : Only in diffusion do molecules. You can see where that would be handy. Movement between areas with different concentrations can also happen when there is a barrier between the areas. A) the cell membrane forms a border between one cell and another in tightly packed tissues such as epithelium. Semipermeable membranes, also termed selectively permeable membranes or partially permeable membranes, allow certain molecules or ions to pass through by diffusion. The charge on a molecule might help or hinder its diffusion, based on the relative charges on either side of the membrane.
Post a Comment for "Solution Or Across A Semipermeable Membrane. Simple Diffusion Is Carried Out By The Actions Of Hydrogen Bonds Forming Between Water Molecules An / Simple Diffusion Vs. Facilitated Diffusion: What's The Difference? - Viva Differences"